2024 recap: Trends, obstacles and opportunities in the GNSS/PNT industry

 (Photo courtesy of ION)
(Photo courtesy of ION) In 2024, we witnessed emerging trends, challenges and opportunities that significantly impacted the GNSS/PNT industry, ranging from advancements in surveying technology to ways to combat the increasing threats of jamming and spoofing. In this year in review, we highlight notable stories from 2024.
To read more, visit our full digital edition archive.
January
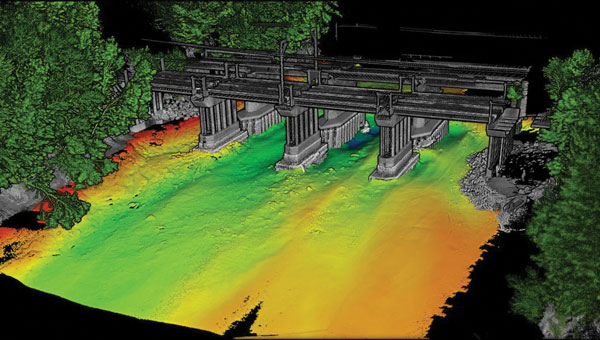
Image: Advanced Navigation
Charting uncharted waters: Bathymetry in action
This article discussed advancements in bathymetric surveying techniques, highlighting three projects — from SBG Systems, CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) and Advanced Navigation — that are charting underwater environments. It showcased the exploration of the Great Blue Hole in Belize using submarine-mounted sonar, creating a digital twin flood model for China’s Yellow River using unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) and UAVs and the development of an autonomous vessel for surveying wet gaps in military operations.
February
Aligning the trades: GNSS for architecture, engineering and construction
Surveying is an ongoing process on construction sites. Surveyors are the first on the site before any other work begins and the last ones there to map the project “as built.” Total stations with GNSS receivers, tablets and other mobile digital devices are their essential tools, increasingly complemented by UAVs and lidar scanners. In this story on architecture, engineering and construction (AEC), we highlighted three building projects — from ComNav Technology, CHCNAV and Eos Positioning Systems — as well as photos from Juniper Systems.

Photo: Safran Federal Systems
March
2024 GPS World simulator buyers guide
In our 13th annual Simulator Buyers Guide, we featured simulator tools, devices and software from nine prominent companies that aid GNSS receiver manufacturers in product design.
April
L5-first for improved resilience in mass market GNSS
Paul McBurney, co-founder and CEO of oneNav, emphasized the advantages of L5-first GNSS receivers in enhancing resilience against GNSS interference and jamming in mass market applications. He shared how traditional receivers prioritize L1 signals, limiting their effectiveness in high-interference environments, while L5 signals, which have a higher chipping rate and power, can improve jamming resistance by up to 15 dB. The article advocated for the development of L5-first systems to boost GNSS resilience, particularly for critical infrastructure, although challenges such as acquisition complexity and cost must be addressed before widespread adoption.
May

(Photo: CAST Navigation)
Combating jamming and spoofing: PNT on the battlefield
Jamming and spoofing continue to be the key challenges to military use of GNSS. While the production and adoption of M-Code receivers is delayed, defense contractors are developing several approaches to identify, locate and neutralize these threats — including CRPA antennas, embedded GPS inertial (EGI) navigators, software-defined radios and cryptography. In this cover story, executives from seven companies presented their perspectives on the GNSS/PNT challenges faced by U.S. and allied military forces, their market niche in this area and their latest products.
June
NextNav petitions FCC for new spectrum band
NextNav’s petition to the FCC seeks to reconfigure the 902-928 MHz band for a new terrestrial positioning, navigation and timing (TPNT) service. This service aims to complement GPS, enhancing location reliability in urban areas. The integration with 5G technology could further improve positioning services. However, the petition has raised significant concerns within the GNSS industry. Industry leaders argue that granting NextNav access to this spectrum could disrupt existing technologies that rely on the same band. The proposed higher power levels could lead to interference, jeopardizing the operational reliability of various sectors, including supply chains and healthcare. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has received more than 1,700 comments highlighting concerns about harmful interference and calling for careful evaluation before any regulatory changes are made. The outcome of this petition could significantly influence the future landscape of positioning technologies in the United States, affecting both GNSS capabilities and the viability of critical applications that depend on current spectrum usage.
July
PNT without GNSS
For the fourth year in a row, the topic for our July cover story was complementary positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). The ongoing challenges of combating jamming and spoofing, as well as enhancing resilience in PNT systems, have been prominent themes in our articles and industry throughout 2024. The U.S. National Space-Based Positioning, Navigation and Timing Advisory Board has been actively working on strategies to “protect, toughen and augment” GPS. The term “augment” refers to enhancements made to GPS and the integration of complementary PNT sources that can partially or fully replace GPS. For this cover story, Editor-in-Chief Matteo Luccio interviewed executives from four companies that design, produce and operate various complementary PNT technologies, highlighting their diverse approaches to this challenge.

Genesis satellite.
August
Innovation: ESA’s Multi-Modal space mission to improve geodetic applications
The European Space Agency (ESA) has established the Genesis mission, a groundbreaking space project that will collocate four space-based geodetic techniques — GNSS, VLBI, SLR and DORIS — on a single satellite for the first time. This mission aims to improve the accuracy and stability of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) to 1 millimeter with long-term stability of 0.1 mm per year, which is crucial for detecting small variations in Earth’s solid, fluid and gaseous components. The Genesis satellite, set to launch in 2028, will orbit at an altitude of about 6,000 km with an inclination of 95° and will operate for at least two years. Members of the Genesis mission team shared how it has the potential to significantly impact various GNSS and Earth observation applications by improving geodetic and geophysical observations, as well as enhancing precise navigation and positioning capabilities.

(Photo courtesy of ION)
September
ION GNSS+ 2024
ION GNSS+ 2024, held Sept. 16-20 at the Hilton Baltimore Inner Harbor, showcased more than 400 technical presentations spanning six sectors. GPS World had the opportunity to engage in a series of discussions and panels, including a plenary session with a presentation on a space project and one on circumnavigating the globe in a sailboat using only paper charts, a compass and a sextant to navigate.
INTERGEO 2024
The GPS World team touched down in Stuttgart, Germany, for INTERGEO 2024, held from Sept. 24-26. This year’s expo and conference showcased solutions to address critical global issues such as GNSS jamming and spoofing. GPS World Publisher Brian Kanaba and Account Manager Tim Carolin made their debut at the show, joining show veteran Editor-in-Chief Matteo Luccio. The show attracted more than 17,000 visitors from 121 countries and featured 579 exhibitors.
October
Lidar helps unlock secrets in Amelia Earhart mystery
The October edition of “Mapping Marvel” focused on research conducted for The Discovery Channel’s documentary, “Finding Amelia.” This film explores the latest expedition aimed at uncovering the mysterious fate of Amelia Earhart. It featured contributions from SPH Engineering and investigated the theory that Earhart and her navigator, Fred Noonan, may have crashed in Papua New Guinea during their 1937 attempt to circumnavigate the globe.
The team utilized lidar technology to conduct low-altitude flights that produced detailed maps of the ground beneath the dense jungle. This approach revealed potential hidden features, including Japanese troop trails and a structure resembling Earhart’s Lockheed Electra.
November

Richard Langley
The last one: A look back at 35 years of ‘Innovation’
The November 2024 issue of GPS World featured Professor Richard Langley’s 300th and final “Innovation” column. His first one appeared in the January/February 1990 issue, the magazine’s very first. In celebration of Richard’s decades-long contribution to GPS / GNSS / PNT, we published a selection of testimonials and photos from some of his colleagues and friends, gathered by his former students Sunil Bisnath and Attila Komjathy.
December
Directions 2024: GNSS constellation updates
This year’s “Directions” feature offers updates on all four GNSS constellations and a regional one. Representatives from each program — BeiDou, GPS, Galileo, GLONASS and QZSS — reflect on the year’s developments, sharing how PNT technologies aim to enhance both defense and civilian applications, ultimately improving navigation capabilities worldwide. The feature highlights significant milestones, including the modernization efforts within each constellation.
















Follow Us