No audio available for this content.
Each day, millions of transportation decisions are made without a driver manually choosing a route or reacting to road signs. Trucks are rerouted around traffic hours before a jam appears. A vehicle slows down in a school zone, even without seeing a sign. A delivery service dynamically dispatches drivers based on weather and wait times.
These are not just conveniences; they are outcomes of location intelligence working behind the scenes, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and real-time mapping.
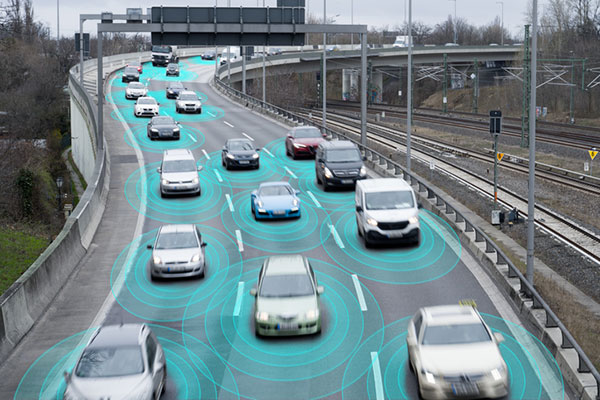
At the heart of these systems lies a fundamental shift: maps are no longer static guides for humans. AI is unlocking a new era of computing and autonomous systems that will drive industry innovation and reinvention for years to come. Maps have become live, machine-readable software that enables automation at scale. Accenture’s Technology Vision 2025 report found large-language models (LLMs) are giving machines and robots more autonomy in the physical world, allowing them to better understand the physics of their environments, have spatial awareness, interact with people and understand complex instructions. This evolving autonomy is critical for autonomous vehicles, smart logistics and other systems that rely on real-time, AI-powered mapping to sense, decide and act.
Whether it’s advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), predictive logistics, EV range optimization or smart city operations, AI-powered mapping is fast becoming the connective tissue between sensing, decision-making, and action. It all begins with location data that is collected, interpreted and delivered in real time.
From Navigation to Infrastructure: The Evolution of the Map
Throughout the past two decades, digital maps have evolved from a novelty to a necessity. The early wave of turn-by-turn GPS tools was designed for humans — to get us from one point to another using the shortest or fastest route.
Today, we are witnessing a new paradigm. As autonomy becomes embedded in vehicles, delivery operations, and mobile robotics, we need a new kind of map — one built for machines.
These maps must be able to see, react and even predict. They must be continuously updated with real-time inputs, capable of interpreting events and structured in a way that allows for automation logic. In other words, they must be intelligent; and that intelligence comes from AI.
AI-Powered Maps: What Makes Them Different?
A live, AI-powered map is far more than a digital representation of roads and intersections. It begins with a foundational base layer — detailed information about road geometry, lanes, speed limits, signage and more. However, what sets these maps apart is how they evolve in real-time to reflect the dynamic nature of the world around us.
They incorporate constantly changing inputs like traffic flow, construction activity, road closures and weather conditions — data streams that traditional static maps cannot accommodate. Beyond reacting to real-time events, AI maps also understand context. They may recognize nuances such as school zones that change by time of day, hazardous intersections, low-clearance bridges, and the availability or compatibility of EV chargers at nearby locations.
Crucially, AI-powered maps don’t just describe what’s happening – they anticipate what might happen next. Fueled by billions of data points collected from vehicles, sensors, satellite imagery and crowdsourced sources, these systems use predictive modeling to foresee traffic build-ups, potential hazards or shifts in road accessibility.
The result is a map that doesn’t merely guide but thinks — a constantly updating model of the world designed not for human eyes alone, but for machines that need to make decisions in real-time.
AI fuses these elements, constantly recalculating and enriching the map to reflect what’s happening now and what might happen next.
For this to work, mapping platforms must ingest the billions of data inputs. AI models then validate, filter and extract insight from this data — turning raw input into actionable intelligence and guidance.
Why AI Maps Matter in the Vehicle
Modern vehicles are increasingly defined by software, and that software needs a constant, reliable connection to the outside world.
ADAS features, such as intelligent speed assistance (ISA), lane keeping and predictive cruise control, depend not only on sensors like cameras or radar, but also on high-quality map data to anticipate what’s ahead.
For example, speed limit detection based solely on onboard vision can fail in poor weather or when signs are obscured. But when paired with verified, map-based data, continuously updated by AI, vehicles can make safer, more consistent decisions. As regulators in the EU and beyond mandate ISA systems in new vehicles, AI-enhanced maps are becoming a tool for regulatory compliance, not just convenience.
As OEMs continue their shift toward software-defined vehicles (SDVs), they increasingly treat maps as a core software module, critical to the operation of the vehicle itself, not just a navigation layer.
In the era of SDVs, maps are evolving into a foundational software service used not just to get somewhere, but to determine how and when it is safe to drive.
How AI Maps Support the EV Transition
One of the most significant barriers to widespread EV adoption is range anxiety: the fear that a driver won’t reach a charger in time, or that the charger will be in use or out of order. AI-powered maps help directly address this.
By combining real-time charger availability, plug compatibility, dynamic traffic conditions, topography, and vehicle battery status, intelligent routing systems can not only suggest optimal charging points, but also reroute on the fly as conditions change.
This level of intelligence is essential for EV fleet operators, especially those in logistics, ride-hailing or municipal transit.
AI-powered maps also leverage charger usage patterns, traffic flows and gaps in the network to help cities plan where to place new charging infrastructure.
In this way, location intelligence doesn’t just support EVs on the road but helps accelerate adoption.
Why AI Maps Matter in the Supply Chain
A HERE Technologies ‘On the Move’ survey found only 25% of transportation and logistics professionals are leveraging AI in supply chain management. Yet, the use cases for AI-powered mapping are plentiful.
Fleet operators face daily challenges: delays, emissions targets, labor shortages and delivery windows that shift by the hour. They’re actively seeking technology-based solutions. McKinsey projects the autonomous heavy-duty trucking market could reach an aggregated $616 billion in 2035 in China, the United States and Europe.
AI-powered maps help address many of these challenges. By combining real-time traffic information, road restrictions (e.g., weight limits, low bridges), and predictive analytics, intelligent maps help logistics operators optimize every mile.
For example, dynamic routing can avoid areas of congestion hours before they peak, based on machine learning models trained on historical and live data. AI can prioritize delivery orders based on customer availability, time-of-day restrictions or weather disruptions.
Beyond routing, maps also assist in asset tracking and risk management. Telematics systems that combine GNSS positioning with AI-based location intelligence can detect anomalies in driving behavior, flag out-of-route events and improve operational safety.
The results are evident and tangible: lower fuel consumption, reduced delivery times and higher fleet utilization.
GNSS and Geospatial Foundations
It’s important to underscore that these intelligent maps still depend on foundational technologies like GNSS. Without reliable satellite-based positioning, none of these applications (ADAS, EV routing or predictive logistics) would be possible.
But GNSS alone isn’t enough. Real-time location must be contextualized. An accurate lat/long fix is powerful, but the system needs to know: What road is that on? What’s the speed limit? Are there known hazards? What time of day is it? Is it raining?
This is where geospatial data, fused with AI and layered into live maps, becomes transformational. The future isn’t about replacing GNSS — it’s about expanding what’s possible when GNSS is augmented with AI, context and prediction.
Looking Ahead: Mapping as Mission-Critical Infrastructure
As autonomy increases across industries — from fully autonomous vehicles to self-driving delivery trucks to smart city systems — AI-powered maps will underpin critical operations.
AI-powered maps will be essential to the flow of goods, the safety of passengers and the predictability of city infrastructure. These systems must be continuously updated, machine-readable, context-aware, predictive and scalable. They also must be built with privacy, security and compatibility in mind. Governments, automotive manufacturers, technology providers and mapping platforms will need to collaborate — not just on data collection, but on standards, governance and interoperability.
Quiet Engine of Autonomy
We often focus on the visible outputs of automation: the driverless shuttle, the drone delivery, the smart traffic signal. However, none of these can function without a live map underneath, enabling every decision, in every moment.
Digital maps have become the quiet engine of autonomy. With the power of AI, they’re becoming smarter, faster and more essential every day.
For professionals in GNSS, geospatial intelligence, and positioning systems, this shift opens new territory where location isn’t just about where things are, but also about what’s happening, why it matters and what should happen next.
In this world, AI-powered maps are no longer a tool. They’re infrastructure.