No audio available for this content.

Upholding the principles of “superior construction, excellent management, and substantial development,” the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) implements multifaceted strategies to ensure uninterrupted and stable system operations and services, with its backup satellites launched into orbit as per the scheduled plan in 2024. Concurrently, research on next-generation BDS technology upgrades and related technological trials for integration with low-Earth orbit (LEO) positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) systems are vigorously promoted, further enhancing international collaboration and propelling the continuous advancement of BDS in the new era.
1. System operation and services
BDS currently consists of 45 operational satellites in orbit, delivering services through 15 BDS-2 and 30 BDS-3 satellites. Since May 2023, five BDS-3 backup satellites have been launched to bolster system resilience.
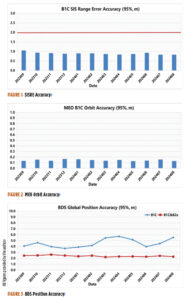
According to the monitoring data from the International GNSS Monitoring and Assessment System (iGMAS) and the International GNSS Service (IGS) in 2024, BDS achieves a service availability of 100% and exhibits a single satellite signal continuity of 99.991% per hour, with signal-in-space accuracy surpassing 0.9 meters (95%), broadcast ephemeris accuracy surpassing 0.2 m (95%), single frequency three-dimensional positioning accuracy of the B1C signal better than 6 m (95%, global average), and the B1C/B2a dual-frequency three-dimensional positioning accuracy superior to 3 m (95%). The timing accuracy is noted to be better than 10 ns (95%). The performance of the BDS PNT service has consistently met all performance requirements.
Figure 1 illustrates the spatial signal accuracy of the BDS B1C signal. Figure 2 presents the broadcast orbit accuracy of the BDS B1C signal. Figure 3 showcases BDS’ global positioning accuracy for both single-frequency and dual-frequency.
Through the BeiDou Satellite-Based Augmentation System B1C (BDSBAS-B1C) and the BeiDou Satellite-Based Augmentation System B2a (BDSBAS-B2a) signals, BDS offers single-frequency BDSBAS service that meets APV-I requirements and a dual-frequency multi-constellation service that meets CAT-I requirements for China and surrounding regions. The ionospheric grid model has been persistently refined to enhance the performance of the satellite-based augmentation services at the peripheries. Evaluation results reveal that the BDSBAS service attains a single-frequency positioning accuracy of 1.29 m (95%) horizontally and 1.99 m (95%) vertically, and a dual-frequency positioning accuracy of 0.77 meters (95%) horizontally and 1.41 m (95%) vertically.
BDS disseminates precise orbit and clock difference corrections and inter-code biases via the precise point positioning (PPP)-B2b signal, providing PPP services to China and surrounding areas. Evaluation results indicate that the BDS-only precise point positioning accuracy is 0.16 m (95%) horizontally and 0.22 m (95%) vertically, with a convergence time of less than 20 minutes.
In 2024, building upon its PNT services, BDS actively offers diversified specialized services, including regional short message communication, global short messaging, and international search and rescue. The number of user terminals for regional short message communications continues to grow. Based on inter-satellite links, global short messaging services can provide users with global random-access capabilities. These services have been applied in projects such as the Einstein Probe mission, the SVOM satellite in collaboration with France, and gravitational wave detection satellites, achieving instant return of global detection data. While six medium-Earth orbit (MEO) satellites are equipped with international maritime search and rescue payloads, the BDS return link enables transmission with a communication delay of less than 12 seconds, and a success rate of 96.82%, suitable for distress alert feedback, disaster information broadcasting and other multi-application scenarios.
The stable BDS operation ensures the consistent and rapid improvement of application industries and the expansion of application scenarios. In 2023, the total output value of China’s satellite navigation and location-based service industries reached more than RMB 530 billion, marking a growth of more than 7% compared to 2022.
2. System construction and development
In May 2023, a backup geostationary orbit (GEO) satellite was launched, followed by two additional MEO backup satellites launched in December 2023, featuring upgraded global short message communication capacity and enhanced intelligent payload technologies. These backup satellites have successfully completed in-orbit testing and are now ready to provide services as needed. In September 2024, another pair of MEO backup satellites, equipped with innovative atomic clocks and a new type of inter-satellite links, were deployed. These backup satellites improve system reliability and service performance and facilitate experimental validation for next-generation satellite technology upgrades.
To continuously enhance system service performance, BDS has developed precision and stability enhancement plans for both the ground control system and the in-orbit satellite support system. Efforts include intensifying satellite-based and ground-based multi-source data fusion analysis, conducting regular assessments of constellation and ground system statuses, and improving fault automatic diagnosis, response efficiency, and intelligence capacity.
China is actively promoting the integrated development and experimental validation of BDS and LEO satellite navigation augmentation systems. Leveraging several test satellites within the under-construction LEO constellation, experiments including GNSS+LEO FPPP have been conducted. Results demonstrate that GNSS orbit determination accuracy is better than 5 cm (1σ), and clock error determination accuracy is superior to 0.15 nss (1σ). With signal enhancement from two to three LEO satellites, PPP positioning accuracy reaches 0.3 m with a convergence time at the minute level, thereby enhancing high-precision service performance and reducing PPP convergence time.

3. International coordination and cooperation
China has been deeply involved in international satellite navigation. Since 2023, China has actively participated in a series of events under the United Nations framework, including the ICG-17 and the United Nations Workshop on the Application of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, contributing to the global advancement of satellite navigation. China has engaged in deep collaboration with system providers from the United States, Russia and the European Union to facilitate compatibility and interoperability, covering navigation signal structures, time systems, coordinate frameworks, test and assessment. Meanwhile, discussions are held with regional navigation satellite systems and emerging systems on topics of mutual interest, such as high-precision services and emergency alert services. In 2024, the BDS timing service was officially included in the Time Bulletin by the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM), signifying international recognition of the ability to provide precise and reliable standard time services globally.
China continues to expand its international partnership with BDS. In recent years, events including the BDS/GNSS Global Partner Forum, the China-Africa BDS Cooperation Forums, the China-Arab States BDS Cooperation Forums, the China-Central Asia BDS Cooperation Forums, the International Training Workshop on BDS Technologies and Applications in the Belt and Road Countries and Regions and the International Summit on BDS Applications have been held to share the benefits of BDS/GNSS applications globally.
BDS will continue to uphold the vision of “a first-class navigation satellite system developed by China and dedicated to the world.” It will make every effort to ensure the stable operation, steady upgrades, and advancements of the system, as well as in-depth research in technologies such as low-orbit PNT and lunar PNT, furthering the commercialization, industrialization, and internationalization of BDS applications